The healthcare domain is on an innovation drive. The industry is seeing technology create an impact in every direction: security, predictiveness, accessibility, and affordability.
Now when we talk about technologies changing the healthcare industry for the better, we often talk in terms of blockchain, AI, IoT, etc., but cloud computing acts as a backbone for all these next-gen technological innovations, and it is one of the all-time technological trends of the healthcare domain.
“Markets and Markets predict that by 2027, the market for cloud computing in the medical field will reach $89.4 billion with an average CAGR of 17.8%.”

In this article, we are going to investigate the different facets of cloud computing in healthcare and how it is revolutionizing the domain.
What is Cloud Computing in Healthcare?
Healthcare cloud computing describes the approach of implementing remote server access via the internet to store, manage, and process healthcare data. This process is opposite the one where on-site data centers are established for hosting data on personal computers and provides a flexible solution for healthcare stakeholders to remotely access servers where the data is hosted.
A BCC analysis projects that the global healthcare cloud computing market will reach $35 billion by the year 2022, with an annual growth rate of 11.6%.
Shifting to the cloud comes with two-fold benefits for both the provider and the patient. On the business side, virtualization in cloud computing has proven to be beneficial for both lowering operational costs and enabling healthcare providers to deliver personalized, high-quality care.
The patients, on the other hand, are becoming accustomed to receiving healthcare services immediately. However, cloud computing increases patient engagement by giving them access to their healthcare data, which ultimately results in better patient outcomes.
Read Also: Top 5 Digital Transformation Trends In The Healthcare Industry In 2023 And Beyond
What are the Benefits of Cloud Computing in the Healthcare Industry?
Cloud technology in healthcare answers almost every point that a US adult looks at when engaging with a healthcare service provider.
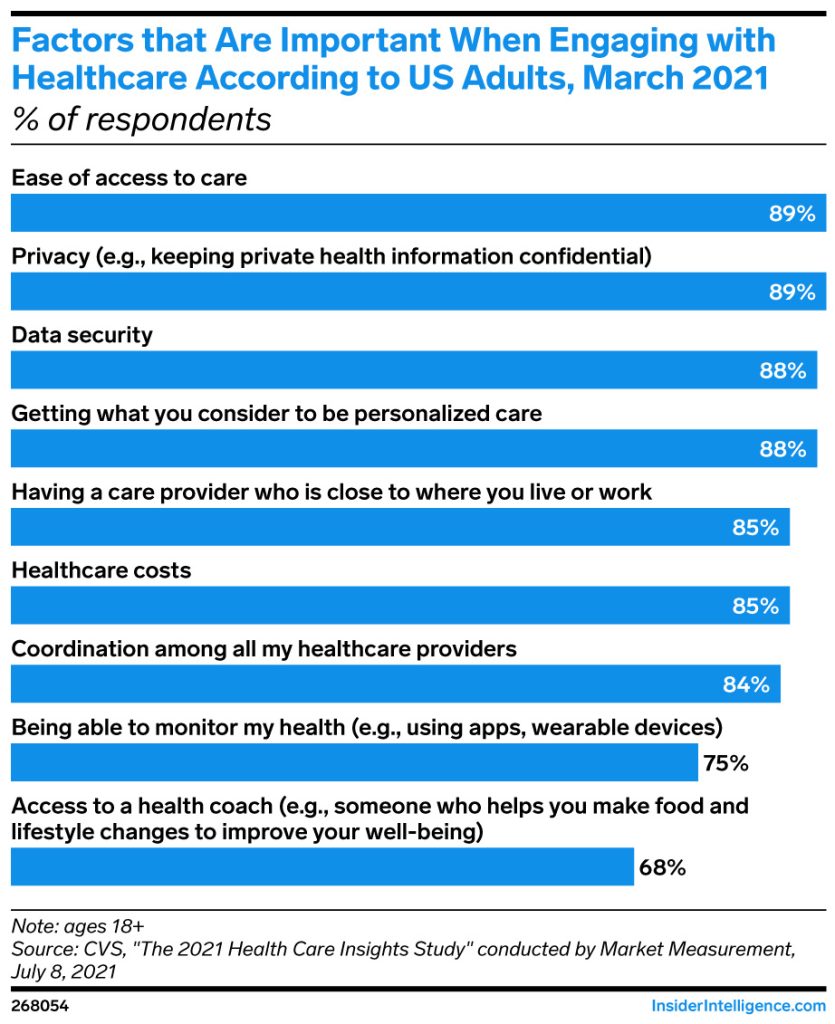
- Lowered healthcare cost
The primary premise of cloud healthcare services is real-time access to computer resources like data storage and computing power. Both Hospitals, as well as healthcare providers, get freed from the need to purchase hardware and software for data storage. Moreover, there are no upfront costs associated linked with cloud healthcare, they will only have to pay for the resource they use.
Cloud computing applications provide an optimum environment for scaling without burning a hole in the pocket. As patient data flows in from not only EMRs but also through healthcare apps and wearables, a cloud environment allows the storage to be scalable without increasing costs.
- Simple interoperability
Data Interoperability focuses on establishing data integrations through the entire healthcare system, regardless of where the data originates or is stored. Cloud-based Interoperability makes patients’ data available for easy distribution and analyzed to aid healthcare delivery.
Through cloud computing, healthcare providers can access patient data gathered from multiple sources, share it with key stakeholders and deliver timely protocols.
- Patient’s Ownership of Data
With a combination of healthcare data and cloud computing advancements, patients can better manage their health. As a result, the patient is more likely to participate in health-related decisions. This tool enhances better patient engagement and education.
The importance of cloud computing in healthcare can be well determined by the medical data that is archived and retrieved easily when it is stored on the cloud. As the system uptime increases, the data redundancy decreases to a large extent, and data recovery also becomes simplified.
- Improved Collaboration
Cloud implementation for healthcare plays a major role in boosting collaboration. Saving Electronic Medical Records on the cloud makes patients more independent in carrying their medical records to every doctor visit. The doctors can easily view the information, analyze the outcomes of previous interactions, and even share information in real time. This information enables doctors to provide more accurate treatment.
- Enhanced Patient Experience
With the help of the cloud, doctors get the power to improve patient engagement by providing them with real-time access to medical data, test results, and even doctors’ notes. This gives the patients better control over their health as they become more educated about their health.
A cloud-based healthcare system can also keep patients from being overprescribed or dragged through unnecessary tests; both can be documented in medical records.
Now that we have a clear understanding of the benefits associated with cloud computing in healthcare, the next step is to learn about the different types of cloud computing in healthcare.
Types of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cloud computing for the healthcare industry works in two defined models: Deployment and Distribution.
1. Cloud Computing Model: Deployment

There are four approaches to this model. It includes:
- Private
The private approach provides the data to only one healthcare firm/ chain that can use the cloud computing facility.
- Public
The public model of deployment includes accessibility of the cloud and is open to all healthcare stakeholders.
- Community
A group of healthcare bodies can access the data stored in the cloud
- Hybrid
This model of deployment combines the elements of all the above-mentioned deployment models for better accessibility to healthcare data.
2. Cloud Computing Model: Distribution
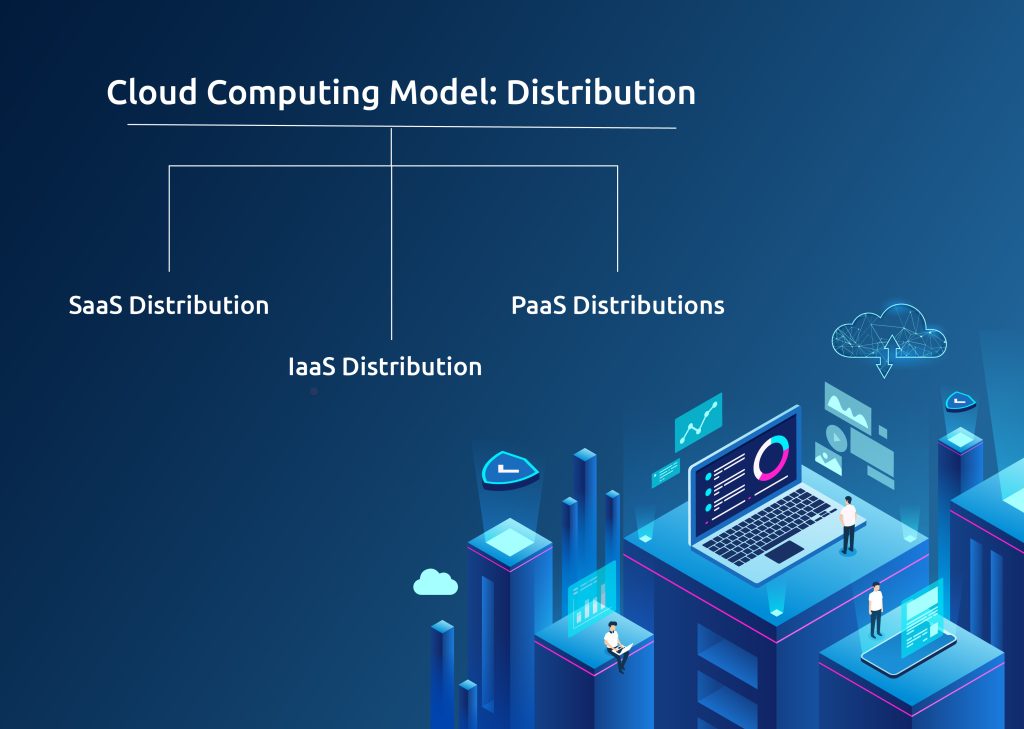
There are three approaches to this model. It includes:
-
SaaS Distribution:
Software as a Service or SaaS providers offer an IT infrastructure where the client can deploy their applications
-
IaaS Distribution:
An Infrastructure as a Service provider gives an IT infrastructure and operating system that helps the client deploy their applications.
-
PaaS Distributions:
Platform as a Service provider delivers the IT infrastructure, the operating systems, necessary applications, and all the components required and ready to use as a platform.
Patient Engagement Solution-A Working Example of the Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Being a renowned cloud technology healthcare provider, the Techspian team understands the ins and outs of the industry and the technological impact of cloud computing.
We recently transitioned this knowledge into a solution aimed at interactive patient engagement.
The fully customizable patient engagement solution improves patient outcomes and makes the work of the healthcare team safer and simpler. We hoped to achieve a stress-free patient engagement ecosystem and a superior customer experience with this software.
The result is that our client pCare has reported tremendous success, including a smooth implementation process, positive responses from hospitals, clinicians, and patients, and a measurable ROI.

In addition to discussing the benefits of cloud healthcare solutions, it is important to appreciate the risks as well as truly understand the technology’s role in healthcare.
Risks of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
- Inadequate Knowledge
It is difficult to find expert software developers in the healthcare domain who are capable of integrating new technologies into the industry. Also, it’s tough to find cloud professionals in the health domain.

- Restricted Ecosystem
In the healthcare industry, the acceptance of cloud solutions cannot make the whole industry productive and efficient. To reap the benefits of this technology, healthcare organizations need to use artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and data management technologies.
- Issues in Adopting Technologies
Switching from the legacy framework to cloud technologies needs to transform the whole task management process. Healthcare organizations must teach everyone how to use it in their daily tasks.
- Security Challenges
Storing healthcare data in the cloud is at the center of the technology’s adoption. However, it comes with security risks as well.
It happens due to the primary cloud setup, a company’s data may be shared on the server with other companies, and the remote systems to individualize them may fail. It causes a situation where healthcare organizations fail to adopt cloud solutions.
Why Partner with Techspian Services?
Techspian services utilize two decades of experience to provide best-in-class cloud software development services and help build reliable, scalable, and secure solutions. Our team has been working hard to improve clinical and business operations for both healthcare institutions and practitioners.
Here are a few things that set us apart from other healthcare IT providers
- An ideal blend of technical experience, talent, and domain knowledge
- Agile processes and thorough quality control
- Optimized solutions within budgets
- Customization to meet client’s specific needs