BLOG
Top 5 Digital Transformation Trends in the Healthcare Industry In 2023 and Beyond
Top 5 Digital Transformation Trends in the Healthcare Industry In 2023 and Beyond
In healthcare, digital transformation implies a technology upgrade. Many healthcare institutions adopted digital transformation over the past decade. However, in many situations, they implemented technologies in silos.
Let’s say there is a dialysis patient suffering from Kidney failure. The Emergency Department (ED), primary care doctor, and dialysis unit have patient medical records.
The ED and primary care unit doctor has shared an Electronic Health Record (EHR). But the discharge note says little information about his care, medications, and the communication between the departments. The patient’s medical condition says he needs a kidney transplant.
This kind of piecemeal initiative hospitals followed over some years. That has serious consequences for many patients. However, the pandemic shook the healthcare system, altered this status quo. Virtual healthcare, remote monitoring, and consultations became not only a necessity, but also a preference.
This blog will talk about some key healthcare trends and how healthcare companies are solving communication silos and, hence, improving patient care. So, you know what to expect from some of the top players in the industry.
Here are some top 5 healthcare trends that have the potential to transform the industry:
- AI in Healthcare
- Virtual and Augmented Reality in Healthcare
- IoT In Healthcare
- Telehealth and Remote Care
- Wearable Medical Devices
Let’s explore them one by one.
AI in Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence is transforming the way healthcare is being delivered. Hospitals have accumulated vast data in the form of health records, insurance claims, lab reports, and so on.
AI can support physicians in clinical decisions by mimicking their workflow. The real-time data can provide continuous feedback for addressing emergency health conditions on time. AI algorithms can proactively analyze data to reach out to patients with updates on disease progression and advise the best healthcare actions.
The covid-19 restrictions made us rely on digital solutions. The hospitals couldn’t handle many calls and queries on their existing online channels. Hence, governments and healthcare institutions are seen adopting conversational AI.
Conversational AI makes use of Machine Learning (ML) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to automate conversations with the users. It reduces the human interventions to provide basic solutions to the customers.
For instance, conversational AI can assist users with:
- the symptom analysis and the best steps to avoid let’s say — a throat infection
- receive lab results, appointments, and suggested prescription
- track medical equipment, etc.
Virtual Reality (VR) & Augmented Reality (AR) in Healthcare
From self-care to even surgical procedures, AR & VR are already helping to improve many aspects of healthcare. For example, an Illinois-based MedTech firm — Augmedics has developed an AR surgical guidance system. It allows surgeons to see patients’ anatomy as if they have x-ray vision. AR technology eliminates surgeon distractions and reduces their exposure to x-ray radiation.
AR in healthcare allows you to view patient data in 3D models. Whereas VR helps you to simulate the environment. For example, medical institutes use VR for giving hands-on learning experiences to their students. It gives a better understanding of human anatomy.
Some use cases of AR & VR technology in healthcare:
Vein Visualizer – There is an app called Accuvein that provides medical imaging solutions. It allows nurses to view veins using their cameras. That makes it easier for staff nurses to inject the patients.
Virtual Relaxation – Many people go through stress and VR can take you completely into a different world. Virtual reality in guided meditation enables you to relax.
Pre-surgical Data – you can have a holographic visualization of the organs you want to operate on before even making any incisions.
IoT In Healthcare
The Internet of Things (IoT) revolves around the concept of ubiquitous computing. Where electronic devices connect with microprocessors and sensors to share information. For example, hundreds of IoT devices in a hospital can be set up to monitor patient health, take decisions (using AI), and store data to the cloud platform. And the extension of IoT in healthcare is called IoMT.
Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices varies from monitoring devices to pulse oximeters to insulin pumps. Of course, there are more ways to use IoT in healthcare (like remote patient monitoring, wearable devices, medical asset monitoring, and so on).
Use cases:
- Personal Emergency Response System (PERS), also known as the medical alert system can help elderly people who are limited in their movement.
- Wearable devices can prevent elder people from fall detection. Because they are more prone to such injuries.

Source: Apple Watch
- IoMT allows medical asset management by tracking the whereabouts of the equipment. It also keeps track of device maintenance and sends reminders to the asset management team.
Telehealth and Remote Care
Telehealth (also called telemedicine) is where your healthcare provider takes your care using online devices like a smartphone, tablet, or computer. For example, your healthcare provider might give you a device that gathers vital signs to keep a check on your health.
The remote care solution enables physicians to monitor and consult chronic patients while they reside at home. Many symptoms like high blood pressure, heart conditions, diabetes, and asthma — can be tracked using remote monitoring trends.
Some benefits of remote patient monitoring:
- shorten hospital stays with remote care devices to use at home
- fewer visits to hospitals
- preventive measures for chronic conditions
The advancements in telecommunications between healthcare providers and patients has an opportunity to serve underserved populations. According to the Markets and Markets research, the telehealth and telemedicine market estimated to grow at a 26.6 % CAGR to reach 287.5 billion USD by 2027.
Wearable Medical Devices
Wearable devices and their apps have turned wristbands into personalized health clinics. It helps doctors and caretakers monitor your health 24/7 through mobile apps.
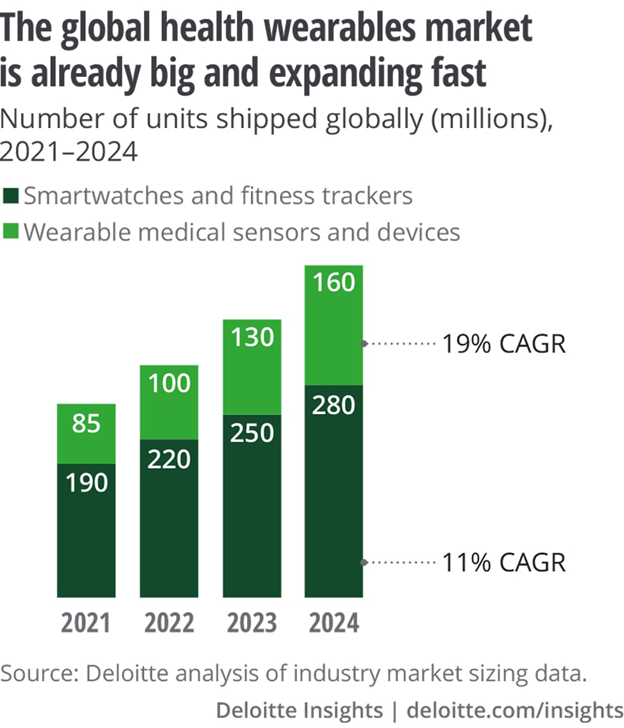
So far, the most common use of wearable technology is a smartwatch – as a fitness tracker. The hospitals have started adopting wearable patient monitoring (e.g., glucose monitors). Many hospitals provide wearable medical devices like wristbands that allow medical staff to access real-time patient information. The device features such as voice commands or text messages enable caretakers to interact with the patients without being physically present all the time.
Patients that are recovering from injuries or surgery, wearable devices help them to stay active. It acts as an encouragement by giving timely reminders.
“The first thing we ought to recognize is that mobile is now part of the fabric — every day in everybody’s life. So, if you’re not looking at mobile solutions, then you’re not really looking at all solutions.” — Mal Postings (Global CTO — IT Advisory Ernst & Young)
Looking Forward
Keeping these healthcare trends in mind, we can aim towards more proactive patient-centric solutions than revenue focused. Time, money, and, more importantly – patient lives are at stake when you think about the digital transformation at your healthcare organization.
As a healthcare provider, you might wonder how to innovate and update your existing systems. Not to worry! We at Techspian focus on developing human-centric experiences through our software services. Our team is specialized in building interactive patient engagement solutions. Get in touch with us, if you are looking to develop a patient-centric healthcare solution!
Related Topics
Trending Topics
Want to build Super app for your business?