BLOG
From Legacy Systems to Next-Gen: How NDC is Reshaping the Airline Distribution
From Legacy Systems to Next-Gen: How NDC is Reshaping the Airline Distribution
What is NDC?
NDC, which stands for New Distribution Capability, is a travel industry standard developed by the International Air Transport Association (IATA). It aims to modernize airline distribution and enhance the communication and exchange of information between airlines, travel agents, and other third-party sellers.
Traditionally, airline ticket distribution has relied on legacy systems and intermediaries, which can be complex and limit the flexibility and personalization of offers. NDC introduces a new framework and protocols that enable airlines to deliver more customized and differentiated products and services to travellers through various distribution channels.

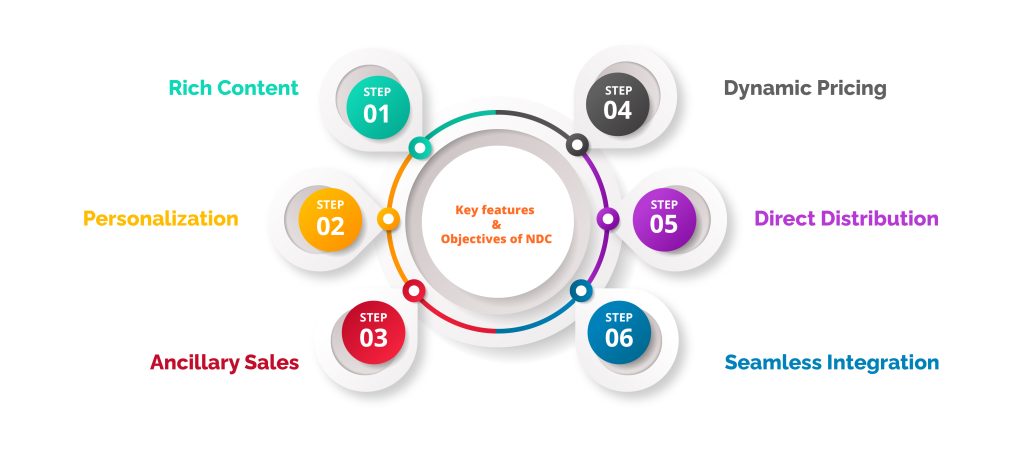
Key features and objectives of NDC include:
Rich Content: New Distribution Capability allows airlines to provide more comprehensive and detailed information about their products and services, including ancillary services, fares, seat selection, baggage options, and more. This enables travellers to make more informed choices.
Personalization: New Distribution Capability facilitates personalized offers and tailored recommendations based on individual traveller preferences, loyalty status, and other relevant data. It enables airlines to deliver targeted promotions and customized packages, enhancing the customer experience.
Ancillary Sales: NDC enables airlines to promote and sell ancillary products and services directly to travellers. This includes options like extra legroom seats, Wi-Fi access, priority boarding, additional baggage, and other ancillaries, which can be bundled or sold separately.
Dynamic Pricing: NDC supports dynamic pricing capabilities, allowing airlines to offer real-time fares and pricing adjustments based on factors like demand, availability, and market conditions. This enhances pricing transparency and enables more flexible and competitive pricing strategies.
Direct Distribution: New Distribution Capability enables direct distribution channels, allowing airlines to connect directly with travellers, bypassing traditional intermediaries. This empowers airlines to have greater control over their distribution strategies, customer relationships, and revenue streams.
Seamless Integration: NDC promotes interoperability and standardized messaging formats, making it easier for airlines, travel agents, global distribution systems (GDS), and other technology providers to integrate and exchange data efficiently.
What does NDC mean for GDS?
NDC (New Distribution Capability) has significant implications for Global Distribution Systems (GDS) in the travel industry. GDS companies have traditionally served as intermediaries between airlines and travel agents, facilitating the distribution of airline tickets and related services. However, with the introduction of NDC, the role of GDS is evolving. Here’s what NDC means for GDS:
Access to Rich Content:
NDC allows airlines to offer more comprehensive and detailed content, including ancillary services and personalized offers. GDS companies need to adapt their systems to accommodate this rich content and provide access to it for travel agents and other users.
Direct Connectivity:
New Distribution Capability enables airlines to establish direct connections with travel agents, bypassing GDS as intermediaries. This direct connectivity allows airlines to deliver personalized offers and customized services directly to travel agents, enhancing the customer experience. GDS companies need to adapt their platforms to support these direct connections and facilitate seamless integration with airline systems.
Technology Upgrades:
GDS companies need to upgrade their technology infrastructure to support the NDC standard. This involves developing and implementing new APIs and messaging protocols that align with NDC specifications. The goal is to ensure compatibility and enable efficient communication between airlines, travel agents, and GDS platforms.
Integration Challenges:
GDS companies must integrate New Distribution Capability capabilities into their existing platforms and workflows. This requires collaboration with airlines to establish data connections, integrate NDC content, and facilitate booking and reservation processes seamlessly. GDS companies need to ensure smooth integration while maintaining compatibility with legacy distribution methods.
Enhanced Offerings and Services:
GDS companies can leverage NDC to enhance their offerings and provide additional value to travel agents and customers. By incorporating New Distribution Capability content and capabilities, GDS platforms can offer a wider range of personalized options, ancillary services, and dynamic pricing, enabling travel agents to provide more tailored and competitive offerings to their customers.
Evolving Role:
With the advent of New Distribution Capability, the role of GDS is evolving from being primarily transactional to becoming more focused on value-added services. GDS companies can provide expertise in NDC adoption, technology integration, and data management, acting as trusted partners for airlines and travel agents as they navigate the new distribution landscape.
What is the New Distribution Capability platform for airlines?
The NDC (New Distribution Capability) platform for airlines refers to the technology infrastructure and systems that enable airlines to implement and leverage the NDC standard. It encompasses the software, protocols, and connectivity required to support direct distribution, personalized offers, and enhanced content delivery to travel agents and other distribution channels.
The New Distribution Capability platform for airlines typically includes the following components:
NDC API: The NDC API allows airlines to expose their content, services, and offers in a standardized format. It enables communication between the airline’s systems and external entities such as travel agents, GDS, and other distribution partners. The NDC API follows the messaging protocols defined by the NDC standard.
Offer Management System: Airlines utilize an offer management system as part of the NDC platform to create and manage personalized offers and fare families. This system enables airlines to define various product attributes, pricing options, ancillary services, and bundles that can be dynamically assembled based on traveller preferences and market conditions.
Order Management System: The order management system within the NDC platform handles the end-to-end process of booking and managing travel orders. It includes functionalities for inventory management, availability checks, booking confirmations, ticket issuance, payment processing, and order modifications or cancellations.
Ancillary Service Management: Airlines use the NDC platform to manage and sell ancillary services such as seat selection, extra baggage, in-flight meals, priority boarding, and Wi-Fi access. The platform allows airlines to define and price these services, integrate them into the booking process, and provide travellers with a seamless ancillary service selection experience.
Content Management System: The content management system is responsible for managing and distributing rich content and product information to the various distribution channels. It allows airlines to showcase their brand, provide multimedia content, and deliver detailed descriptions of products, services, and destination-related information.
Integration and Connectivity: The NDC platform requires integration with the airline’s existing systems, including passenger service systems (PSS), revenue management systems, inventory systems, and other operational systems. It also involves establishing connectivity with distribution partners, GDS platforms, and travel agents to enable real-time data exchange.
What is an example of NDC in travel?
One example of NDC (New Distribution Capability) implementation in the travel industry is the use of NDC-enabled booking platforms or aggregators. These platforms serve as intermediaries between airlines and travel agents, providing a user-friendly interface for browsing and booking flights while leveraging the benefits of NDC. Here’s an example:
Imagine a traveller visiting a popular online travel agency (OTA) website to search for and book a flight. The OTA has integrated NDC capabilities into its platform, allowing it to access enriched content and personalized offers directly from airlines. Here’s how the NDC implementation might work:
Enhanced Flight Search:
The OTA’s NDC-enabled platform provides a more comprehensive flight search experience. It can display detailed flight information, including fare families, ancillary services, seat maps, and real-time availability. The traveller can see more options and make informed decisions based on their preferences.
Personalized Offers:
Leveraging NDC, the OTA platform can present personalized offers tailored to the traveller’s profile, preferences, and loyalty status. For example, the platform may suggest upgrades to premium cabins, offer discounted ancillary services or provide exclusive promotions based on the traveller’s history or preferences.
Dynamic Pricing:
With NDC, the OTA platform can access real-time pricing and inventory data directly from the airlines. This enables dynamic pricing based on factors such as demand, availability, and market conditions. The traveller may see dynamic fare updates as they search and compare flights, ensuring they have the most up-to-date pricing information.
Ancillary Services:
The OTA platform can showcase and sell ancillary services offered by airlines, such as extra baggage, seat selection, or in-flight Wi-Fi. Travellers can conveniently add these services during the booking process, customizing their travel experience to meet their specific needs.
Seamless Booking Process:
Using NDC, the OTA platform facilitates a seamless booking process. The traveller can select a flight, review the fare details, choose additional services, and complete the payment within the same platform. The NDC integration ensures smooth communication between the OTA and the airline’s systems for booking confirmation and ticket issuance.
NDC misconceptions
Misconceptions about NDC (New Distribution Capability) in the travel industry can arise due to the evolving nature of the standard and varying interpretations. Here are some common misconceptions surrounding NDC:
NDC is Only for Direct Bookings:
One common misconception is that New Distribution Capability is solely focused on enabling direct bookings between airlines and travellers, bypassing travel agents or intermediaries. While NDC does facilitate direct connectivity, it also supports indirect distribution through travel agencies, online travel agencies (OTAs), and other intermediaries. New Distribution Capability aims to improve communication and data exchange across the entire distribution chain, benefiting both direct and indirect channels.
NDC is All About Airline Ancillaries:
While ancillary services are an essential aspect of NDC, it is not limited to just ancillary sales. NDC encompasses broader capabilities such as enriched content, personalized offers, dynamic pricing, and enhanced shopping experiences. It allows airlines to provide comprehensive product information, fare families, seat selection, and other services beyond ancillaries. New Distribution Capability focuses on delivering a more personalized and tailored booking experience for travellers.
NDC Replaces Global Distribution Systems (GDS):
There is a misconception that NDC is meant to replace GDS entirely. NDC and GDS can coexist and complement each other. GDS companies are adapting their systems to incorporate NDC content and functionalities, enabling travel agents to access NDC offers through their familiar GDS interfaces. NDC and GDS integration allows for broader distribution and ensures compatibility with existing travel agency workflows.
NDC is Only for Large Airlines:
Another misconception is that NDC is relevant only for large airlines with extensive resources. While larger airlines may have been early adopters of NDC, the standard is designed to be applicable to airlines of all sizes. New Distribution Capability implementation can be scaled to suit the needs and capabilities of individual airlines, allowing them to enhance their distribution capabilities regardless of their size.
New Distribution Capability is a Single Technology or Solution:
NDC is often mistaken as a single technology or solution, but it is a set of standards and protocols developed by the International Air Transport Association (IATA). New Distribution Capability specifies how airlines, aggregators, and systems should communicate and exchange data. It is up to airlines and technology providers to implement NDC in their systems, using various technologies and APIs to achieve the desired connectivity and functionality.
New Distribution Capability Tech Infrastructure: Components and Partners
Implementing NDC (New Distribution Capability) requires a robust tech infrastructure involving various components and partnerships. Here are the key elements involved:
Airlines:
Airlines are the primary stakeholders in the NDC ecosystem. They need to adopt NDC and invest in the necessary technology infrastructure to support it. This includes updating their internal systems, APIs, and messaging protocols to align with NDC standards.
NDC API:
The NDC API serves as the primary interface for communication between airlines and their distribution partners. It allows airlines to expose their content, fares, availability, and ancillary services in a standardized format. The NDC API facilitates real-time data exchange and enables integration with various distribution channels.
Aggregators and Distributors:
Aggregators and distributors play a crucial role in the NDC ecosystem. They act as intermediaries between airlines and travel agents or online travel agencies (OTAs). Aggregators integrate with airlines’ NDC APIs to access enriched content and provide it to their distribution partners. They ensure the seamless flow of data and facilitate the booking process.
Global Distribution Systems (GDS):
GDS companies, such as Amadeus, Sabre, and Travelport, are significant players in the travel industry. They are adapting their systems to incorporate NDC capabilities. GDS providers act as technology partners for airlines, helping them integrate NDC content and functionalities into their existing distribution channels. They enable travel agents to access NDC content through their GDS platforms.
IT Service Providers:
IT service providers and technology companies play a crucial role in assisting airlines with NDC implementation. They offer software solutions, consultancy services, and technical expertise to help airlines adopt NDC standards, develop APIs, upgrade their systems, and ensure seamless integration with partners.
Payment Providers:
Payment providers are essential partners in the NDC ecosystem. They enable secure and efficient payment processing for airline bookings. Integration with payment providers ensures that the NDC infrastructure supports various payment methods and facilitates a smooth payment experience for travellers.
Content Management Systems (CMS):
Content management systems play a vital role in managing and distributing rich content and product information. CMS platforms allow airlines to curate and showcase their brand, including multimedia content, detailed descriptions of products, fare families, ancillaries, and destination-related information. CMS integration with the NDC infrastructure ensures consistent and accurate content delivery.
Booking Engines:
Booking engines, whether operated by airlines or third-party providers, handle the end-to-end process of booking and managing travel orders. These systems integrate with the NDC infrastructure to facilitate inventory management, availability checks, booking confirmations, ticket issuance, modifications, and cancellations.
New Distribution Capability Infrastructure
The NDC (New Distribution Capability) infrastructure refers to the technological framework and components that support implementing and operating NDC standards in the travel industry. It involves various systems, interfaces, and protocols that enable airlines, aggregators, and other stakeholders to exchange data, distribute content, and facilitate bookings. Here are the key components of the NDC infrastructure:
NDC API:
The NDC API serves as the primary interface for communication between airlines and their distribution partners. It allows airlines to expose their offers, fares, availability, and ancillary services in a standardized format. The NDC API follows the messaging protocols defined by the NDC standard and enables real-time data exchange.
Offer and Order Management Systems:
Offer and order management systems are integral parts of the NDC infrastructure. Airlines use these systems to create and manage personalized offers, fare families, ancillary services, and bundles. Offer management systems enable dynamic assembly and pricing of products, while order management systems handle the end-to-end process of booking, inventory management, ticketing, and modifications.
Distribution Platforms:
Distribution platforms, including aggregators, GDS companies, online travel agencies (OTAs), and other intermediaries, play a crucial role in the NDC infrastructure. These platforms integrate with airline NDC APIs to access enriched content, fares, and availability. They provide user-friendly interfaces for travel agents and customers to search, compare, and book flights using NDC data.
Connectivity Protocols:
NDC infrastructure relies on connectivity protocols to facilitate seamless data exchange between systems. These protocols include XML (eXtensible Markup Language), SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol), and RESTful (Representational State Transfer) APIs. They ensure standardized and secure communication between airlines, aggregators, GDS, and other distribution partners.
Middleware and Integration:
Middleware and integration solutions play a crucial role in connecting various systems and components within the NDC infrastructure. They handle data transformation, mapping, and routing between different interfaces, ensuring compatibility and efficient flow of information. Middleware solutions enable seamless integration between airlines’ internal systems, NDC APIs, and distribution partners.
Data Management and Analytics:
Effective data management and analytics are essential for the NDC infrastructure. Airlines and other stakeholders need robust systems to collect, store, process, and analyse vast amounts of data generated through NDC transactions. Data management platforms and analytics tools provide insights into customer preferences, booking patterns, revenue management, and performance evaluation.
Security and Payment Systems:
Security is a critical aspect of the NDC infrastructure. Robust security measures, including data encryption, authentication, and authorization, are implemented to protect sensitive customer and transaction data. Payment systems integration ensures secure and efficient payment processing for airline bookings, supporting various payment methods and complying with industry standards.
Infrastructure Scalability and Performance:
The NDC infrastructure needs to be scalable and capable of handling high volumes of data and transactions. It requires reliable hardware, cloud infrastructure, and network capabilities to ensure optimal performance, availability, and response times, especially during peak booking periods.
What are some of the New Distribution Capability Platforms?
In the context of NDC (New Distribution Capability) in the travel industry, there are various NDC platforms available that facilitate the implementation and adoption of NDC standards. These platforms serve as intermediaries between airlines and travel agents, providing access to NDC content, enriched data, and booking capabilities. Here are some examples of NDC platforms:
Travelport Smartpoint:
Travelport Smartpoint is a comprehensive platform that enables travel agents to access NDC content from multiple airlines through a single interface. It integrates with airline NDC APIs and provides a user-friendly environment for searching, comparing, and booking flights using NDC data. Travelport Smartpoint allows travel agents to access and combine NDC and non-NDC content seamlessly.
Amadeus Travel API:
Amadeus offers an NDC-enabled Travel API that allows developers to access NDC content and functionality. The Amadeus Travel API provides a range of services, including flight search, booking, ticketing, ancillary services, and personalized offers. It offers flexibility for airlines and travel agencies to integrate NDC capabilities into their systems and applications.
Sabre Red 360:
Sabre Red 360 is a comprehensive platform enabling travel agents to access NDC and traditional GDS content in a single workflow. It combines NDC and non-NDC content, allowing travel agents to compare and book flights seamlessly. Sabre Red 360 provides a unified interface for searching, pricing, booking, and managing NDC-based airline offers.
Travelfusion:
Travelfusion is an NDC aggregator that connects airlines and travel agents through its platform. It integrates with multiple airline NDC APIs and provides travel agents with access to a wide range of NDC content. Travelfusion offers a unified interface for searching, booking, and managing NDC-based flight offers and ancillary services.
HitchHiker NDC Gateway:
HitchHiker NDC Gateway is a technology platform that enables airlines to distribute their NDC content to multiple distribution partners. It provides a scalable and flexible solution for airlines to connect with aggregators, travel agents, and OTAs through NDC APIs. HitchHiker NDC Gateway handles data integration, connectivity, and distribution of NDC-based offers.
TPConnects NDC API:
TPConnects offers an NDC API platform that facilitates direct connectivity between airlines and travel agents. It enables airlines to expose their NDC content, including fares, availability, ancillaries, and personalized offers. TPConnects NDC API provides a secure and reliable interface for travel agents to search, book, and manage NDC-based flight bookings.
NDC implementation tips: what to consider before getting started
Implementing NDC (New Distribution Capability) in the travel industry requires careful planning and consideration. Here are some key tips to consider before getting started with NDC implementation:
Define Clear Objectives:
Clearly define your objectives for implementing NDC. Determine what you aim to achieve through NDC adoption, such as improving the booking experience, offering personalized offers, increasing ancillary sales, or enhancing distribution capabilities. Having clear objectives will guide your implementation strategy and help measure the success of your NDC initiatives.
Evaluate Technical Readiness:
Assess your airline’s technical readiness for NDC implementation. Evaluate your existing systems, APIs, and infrastructure to ensure they can support NDC requirements. Identify any gaps or necessary updates that may be required to align with NDC standards. Consider factors such as system scalability, data management capabilities, and integration with external partners.
Establish Partnerships:
Identify and establish partnerships with NDC service providers, aggregators, and technology partners. Collaborate with NDC aggregators or distribution platforms that connect you with a wide network of travel agencies and online travel agents. Engage with technology partners specialising in NDC implementation to ensure a smooth and successful integration.
Determine Content Strategy:
Define your content strategy for NDC. Determine what type of content you want to offer through NDC, including fare families, ancillaries, seat selection, and other services. Develop guidelines for consistent and accurate content management. Consider how NDC content will complement your existing distribution channels and ensure coherence across all distribution channels.
Plan API Development and Integration:
Plan the development and integration of NDC APIs. Work closely with your IT team or technology partners to design and develop APIs that adhere to NDC standards. Ensure proper documentation, version control, and testing of APIs. Consider the scalability and performance of your APIs to handle increased transaction volumes as NDC adoption grows.
Train and Educate Staff:
Provide comprehensive training and education to your staff, including sales agents, customer service representatives, and IT personnel. Educate them about NDC standards, functionalities, and benefits. Train them on using NDC tools, APIs, and workflows. Enable them to effectively promote NDC offerings and assist customers with NDC-based bookings.
Ensure Regulatory Compliance:
Familiarize yourself with relevant regulations and industry standards related to data privacy, security, and customer protection. Ensure that your NDC implementation adheres to these regulations. Take necessary measures to protect customer data and comply with privacy requirements.
Monitor and Evaluate Performance:
Continuously monitor and evaluate the performance of your NDC implementation. Track key metrics, such as booking volumes, revenue generated through NDC, customer satisfaction, and adoption rates. Regularly analyse the data to identify areas for improvement, optimize your NDC strategy, and enhance the customer experience.
New Distribution Capability: Key Technologies to Consider
Implementing NDC (New Distribution Capability) in the travel industry involves leveraging various technologies to enable seamless communication, data exchange, and booking capabilities. Here are some key technologies to consider for NDC implementation:
API Integration:
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) play a crucial role in NDC implementation. Airlines need to develop and integrate NDC APIs to expose their content, fares, availability, and ancillary services in a standardized format. API integration enables real-time data exchange between airline systems and distribution partners, facilitating seamless booking experiences.
Messaging Protocols:
NDC implementation relies on messaging protocols to facilitate communication between systems. Some common messaging protocols used in NDC include XML (eXtensible Markup Language), SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol), and RESTful (Representational State Transfer) APIs. These protocols ensure standardized and secure data exchange, supporting the transmission of structured information.
Data Management Systems:
Robust data management systems are crucial for NDC implementation. These systems handle the storage, processing, and retrieval of large volumes of data generated through NDC transactions. They ensure the availability, accuracy, and accessibility of NDC content, fares, inventory, and customer information.
Cloud Computing:
It provides scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency for NDC implementation. Cloud infrastructure enables airlines to handle variable transaction volumes, scale resources as needed, and ensure the high availability of their systems. Cloud-based solutions also support data storage, analytics, and integration with distribution partners.
Personalization and Recommendation Engines:
Personalization technologies enhance the NDC experience by tailoring offers and content to individual travellers. Recommendation engines analyse customer preferences, behaviour, and historical data to provide personalized flight options, ancillary services, and targeted promotions. These technologies enhance customer engagement and drive ancillary revenue.
Payment Gateways:
Secure and efficient payment processing is critical for NDC transactions. Integration with payment gateways allows airlines to accept various payment methods and ensure secure handling of customer payment information. Payment gateways facilitate seamless payment authorization, settlement, and reconciliation for NDC bookings.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
AI and machine learning technologies can be leveraged to enhance NDC implementation. AI-powered algorithms can analyse large datasets to generate insights on customer preferences, demand patterns, and pricing optimization. Machine learning algorithms can automate tasks, improve search accuracy, and enable intelligent customer service interactions.
Analytics and Business Intelligence:
Analytics and business intelligence tools are essential for monitoring, reporting, and analysing NDC performance. These tools provide insights into booking trends, revenue analysis, customer behaviour, and operational efficiency. They help airlines make data-driven decisions, optimize pricing strategies, and enhance their NDC offerings.
Mobile Applications and User Interfaces:
Mobile applications and user interfaces play a vital role in delivering NDC capabilities to travellers. They enable customers to search, compare, and book flights using NDC content. User-friendly interfaces enhance the booking experience, support personalized offers, and provide self-service functionalities.
Blockchain:
While still emerging, blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize NDC by providing enhanced security, transparency, and efficiency. Blockchain can facilitate the secure sharing of data, streamline settlement processes, and enable smart contracts for automated transactions.
Related Topics
Trending Topics
Want to build Super app for your business?